Symbols Used in ER Model

ERD
- The ER data mode was developed to facilitate database design by allowing specification of an enterprise schema that represents the overall logical structure of a database.
- The ER model is very useful in mapping the meanings and interactions of real-world enterprises onto a conceptual schema. Because of this usefulness, many database-design tools draw on concepts from the ER model.
- The ER data model employs three basic concepts:
- entity sets,
- relationship sets,
- attributes.
- The ER model also has an associated diagrammatic representation, the ER diagram, which can express the overall logical structure of a database graphically.
Components of ER Diagram
ER Model consists of Entities, Attributes, and Relationships among Entities in a Database System.
Entity
An Entity may be an object with a physical existence – a particular person, car, house, or employee – or it may be an object with a conceptual existence – a company, a job, or a university course.
1. Strong Entity
A Strong Entity is a type of entity that has a key Attribute. Strong Entity does not depend on other Entity in the Schema. It has a primary key, that helps in identifying it uniquely, and it is represented by a rectangle. These are called Strong Entity Types.
2. Weak Entity
An Entity type has a key attribute that uniquely identifies each entity in the entity set. But some entity type exists for which key attributes can’t be defined. These are called Weak Entity types
Attributes
1. Key Attribute
The attribute which uniquely identifies each entity in the entity set is called the key attribute
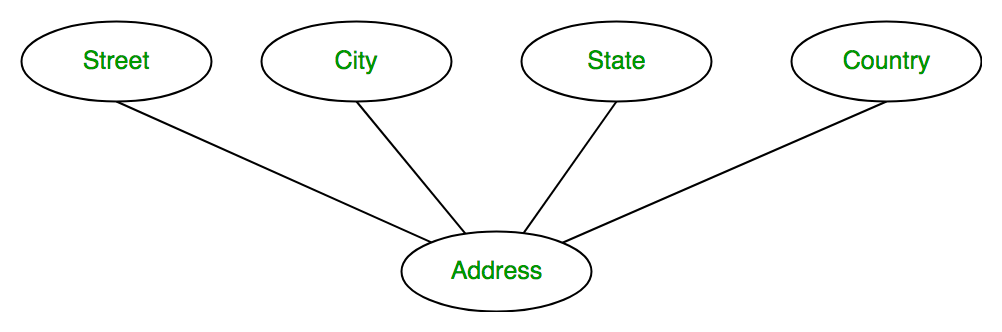
2. Composite Attribute
An attribute composed of many other attributes is called a composite attribute.
3. Multivalued Attribute
An attribute consisting of more than one value for a given entity.

4. Derived Attribute
An attribute that can be derived from other attributes of the entity type is known as a derived attribute.

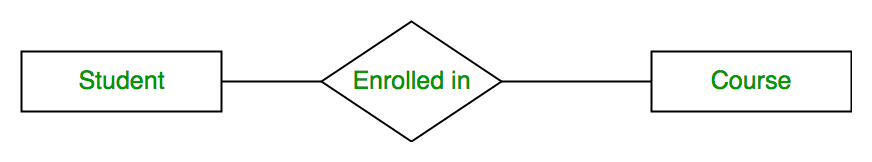
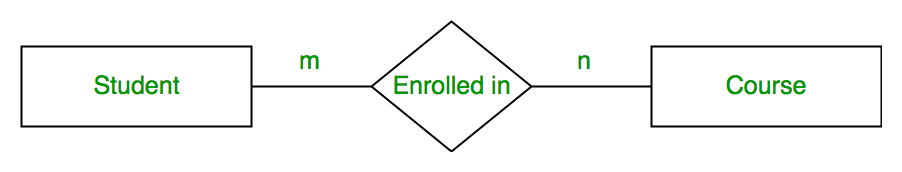
Relationship Type and Relationship Set
Cardinality
The number of times an entity of an entity set participates in a relationship set is known as cardinality. Cardinality can be of different types:
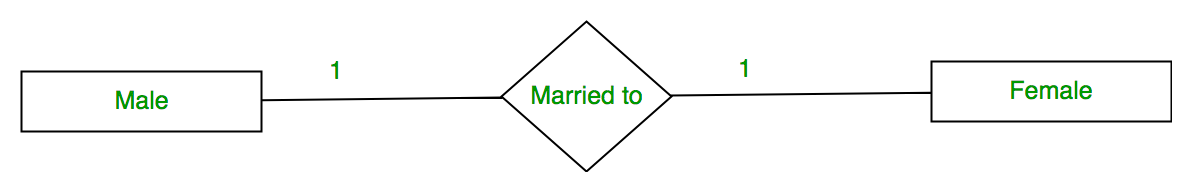
1. One-to-One: When each entity in each entity set can take part only once in the relationship, the cardinality is one-to-one. Let us assume that a male can marry one female and a female can marry one male. So the relationship will be one-to-one.

Key Constraints in DBMS
- Constraints or nothing but the rules that are to be followed while entering data into columns of the database table
- Constraints ensure that data entered by the user into columns must be within the criteria specified by the condition
- For example, if you want to maintain only unique IDs in the employee table or if you want to enter only age under 18 in the student table etc
- We have 5 types of key constraints in DBMS
NOT NULL:ensures that the specified column doesn’t contain a NULL value.UNIQUE :provides a unique/distinct values to specified columns.DEFAULT:provides a default value to a column if none is specified.CHECK :checks for the predefined conditions before inserting the data inside the table.PRIMARY KEY:it uniquely identifies a row in a table.FOREIGN KEY:ensures referential integrity of the relationship
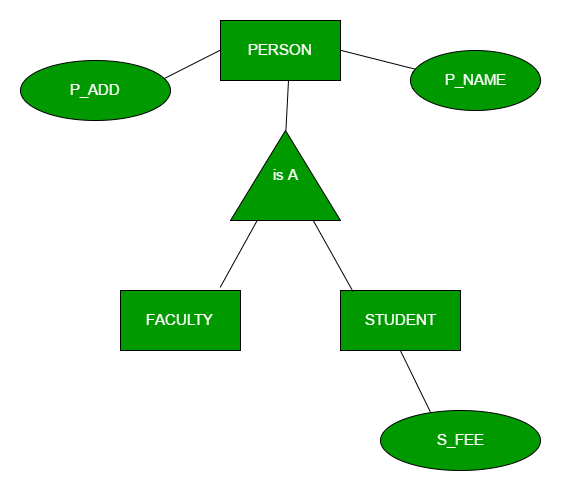
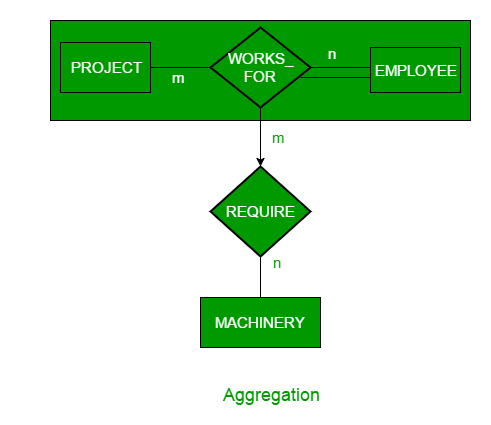
Generalization is the process of extracting common properties from a set of entities and create a generalized entity from it. It is a bottom-up approach in which two or more entities can be generalized to a higher level entity if they have some attributes in common.




Comments
Post a Comment